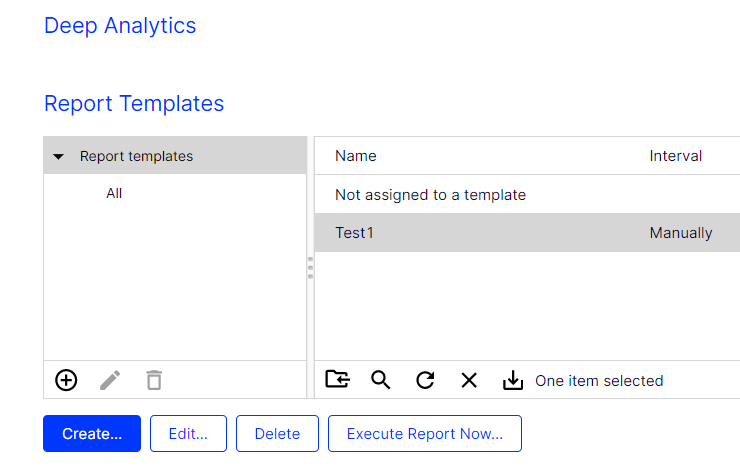
 Creating report templates
Creating report templates
To create a new report template, click Create….
The creation process consists of 3 steps:
To delete a report template, click a report template in the Report Templates list then click Delete. Deleting or changing a template does not affect already executed reports. Reports that are executed from deleted templates are shown as Not assigned to a template in the list.
Step 1. Selecting report data
The Report Data tab lets you define which data is evaluated in a report. You can specify recipients, mailings, measures, and groupings.
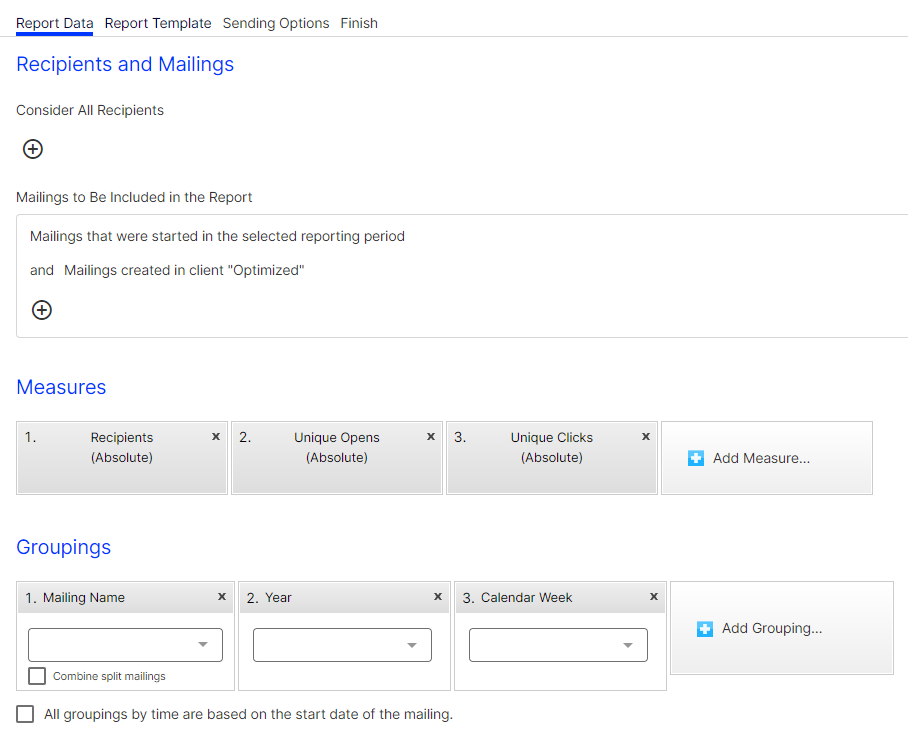
Recipients and mailings
In the Recipients and Mailings area, define recipient segments, mailings, and clients that you want to analyze. If you do not perform the following steps, relevant data is used for the report.
- To analyze recipients by target group, click Add
 below Consider All Recipients.
below Consider All Recipients. - In the list, select a target group and click OK
 .
. - Repeat these steps to use multiple target groups for this report.
Selected target groups are applied to selected clients when the report is executed. This may lead to unwanted results if a target group uses filter rules that do not match recipients in selected clients. See the following mailing example to learn more.
- To analyze certain mailings, click Add
 below Mailings to Be Included in the Report:.
below Mailings to Be Included in the Report:. - To create an exclusive condition (such as is not, contains not, has not), in the left drop-down list, select not.
- In the next drop-down list, you can select the following options.
- ( ... ). Create nested conditions by clicking the parentheses.
- Client. Only available if you have access to more than one client. By default, the client to which you are logged in is selected.
- Folder. Only mailings from specific folders.
- Mailing. Only specific mailings.
- Mailing type. Select one or more mailing types:
- Regular. Optimized mailings of an A/B test (Smart Campaigns) and mailings from Mailings Classics (deprecated).
- Special. Transactional mails.
- Transactional message. Split mailing of a transactional mail. See A/B test for transactional mails.
- Confirmation email. Confirmations.
- Split. Split mailings from Mailings Classics (deprecated).
- Campaign. Mailings and split mailings of a Smart Campaign (without optimized mailings).
To select all mailings of an A/B test in a Smart Campaign, select both options Regular (to select the optimized mailing) and Campaign (to select the split mailings).
- Start date. Select the start date in the next step.
- Reporting period. A reporting period lets you specify the time frame from which data is collected and used for the analysis. By default, only mailings started in the given period are analyzed. If you remove this filter, also opens, clicks, unsubscribes, responses and post clicks that are created from mailings started prior to the reporting period but were only opened, clicked, unsubscribed, and so on within the given period, are analyzed. For the mailings and recipients measures, this difference is irrelevant.
- In the next drop-down list, click the value for the selected filter option.
- To combine several conditions, click Add
 to add a new condition. Between two conditions, an AND or OR logic relation appears, which you can change by clicking it.
to add a new condition. Between two conditions, an AND or OR logic relation appears, which you can change by clicking it. Due to correctness and logical disambiguation, target groups without parentheses can contain only one type of logic relation. Thus, if you click a relation, relations between the rules are changed. If you want to use different types of logic relations, use parentheses.
Parentheses group rules hierarchically to handle them with priority, like in a mathematical equation. Rules within the parentheses are applied first, followed by rules in the second level, and so on. Parentheses are especially useful if a complex condition is planned and different logic terms (AND or OR) will be used.
- Click OK
 .
.
Measures and groupings
Measures "measure" the success of your campaigns and evaluate mailings in detail. Select measures and group them by time period, target groups, click profile, and other factors.
Example: To get an overview of your past mailing activities, you can select in Measures the unique number of recipients, the unique number of opens and, for example, the number of unique clicks. In Groupings, under Date or Time, you can select Year, Calendar week and Date to group the Measure data by time period.
Measures
A measure is defined as a numerical measure of a user interaction (for example openings, clicks or unsubscribes) or characteristic of your mailing (recipients number, sent emails, responses). Measures have the following characteristics:
- Measures are expressed in form of a number.
- Measures are stand-alone entities. If you look at a metric in a stand-alone fashion, it provides information about the overall performance of your mailing.
- Measures form the columns of a report structure.
- You can combine measures in a report.
For a description of available measures, see Measures.
In the Measures area, define measures to be evaluated for this report:
- Click Add Measure…
 .
. - Select a measure from the menu.
- Repeat these steps for measures you want to analyze.
You can drag and drop a measure to the desired position if you want to change it.
Groupings
Groupings (dimensions) have the following characteristics:
- Groupings are non-numerical data fields.
- Unlike measures, groupings are not stand-alone entities, that is, they are not generally meaningful when viewed individually.
- Groupings, when coupled with measures, provide meaningful context to the data.
- Groupings are used to segment a measure.
For an overview and a description of all available groupings, see Groupings.
In the Grouping area, select groupings with which the measures will be matched:
- Click Add Grouping…
 .
. - Select a grouping from the menu.
- In the list, select a value (for example, HM TargetGroup) if you want to specify the grouping more exactly.
- Repeat these steps for groupings the report will evaluate.
Time-based reports
To arrange recipient-specific actions (such as, opens) for a mailing according to the start date of the mailing (mailing-time-based analysis), select the All groupings by time are based on the start date of the mailing check box.
If you clear the check box, recipient-specific actions are arranged separately according to when they occurred (time-action-based analysis).
- Mailing "New Year Newsletter" was started on 01/01/2018.
- Mailing "Information Newsletter" was started on 06/02/2018.
- Time-action-based analysis (check box cleared):
Calendar week Mailing Opens (absolute) 01/2018 New Year Newsletter 5 03/2018 New Year Newsletter 5 04/2018 New Year Newsletter 10 06/2018 Information Newsletter 5 08/2018 Information Newsletter 5 09/2018 Information Newsletter 5 - Mailing-time-based analysis (check box selected):
Calendar week Mailing Opens (absolute) 01/2018 New Year Newsletter 20 06/2018 Information Newsletter 15
Removing doublings
You can remove double counts from the Click Profile, Link, and Target Group groupings automatically.

For example, a recipient in the target groups Men and Age 30-40 years is counted twice if you use both target groups in a report. Thus, the sum line contains doublings. To prevent this, select the Remove doublings check box in the grouping, so the report shows only one match for an arbitrary (applicable) target group of a recipient.
- The recipient belongs to the target groups "Men" and "Age 30-40 years".
- If you clear the Remove doubling check box, the following is shown in the report:
Target Group Recipients (absolute) Men 1 Age 30-40 years 1 Sum line 2 - If you select the Remove doubling check box, the following is shown in the report:
Target Group Recipients (absolute) Men 1 Age 30-40 years 0 Sum line 1
Combinations
You can combine multiple groupings to get multidimensional reports. For example, select the groupings Mailing and Target Group to get a report that shows measures per mailing and for each target group.
User-defined arrangement
The arrangement of groupings affects the result of the report. You can drag and drop selected groupings to the desired position. If you commute the groupings Mailing and Target Group, you get an evaluation of target groups and each target group is evaluated according to mailings.
Calculation of rates
To calculate rates (as percentages), such as open or click rates, make sure to select a grouping that delivers meaningful report data. For example, to get the open rate (as percentage) of a mailing, the Mailing grouping must be selected. In the same way, the open rate by target group can be displayed. However, open rates in a time-based report do not deliver meaningful values.
Step 2. Configuring the report template
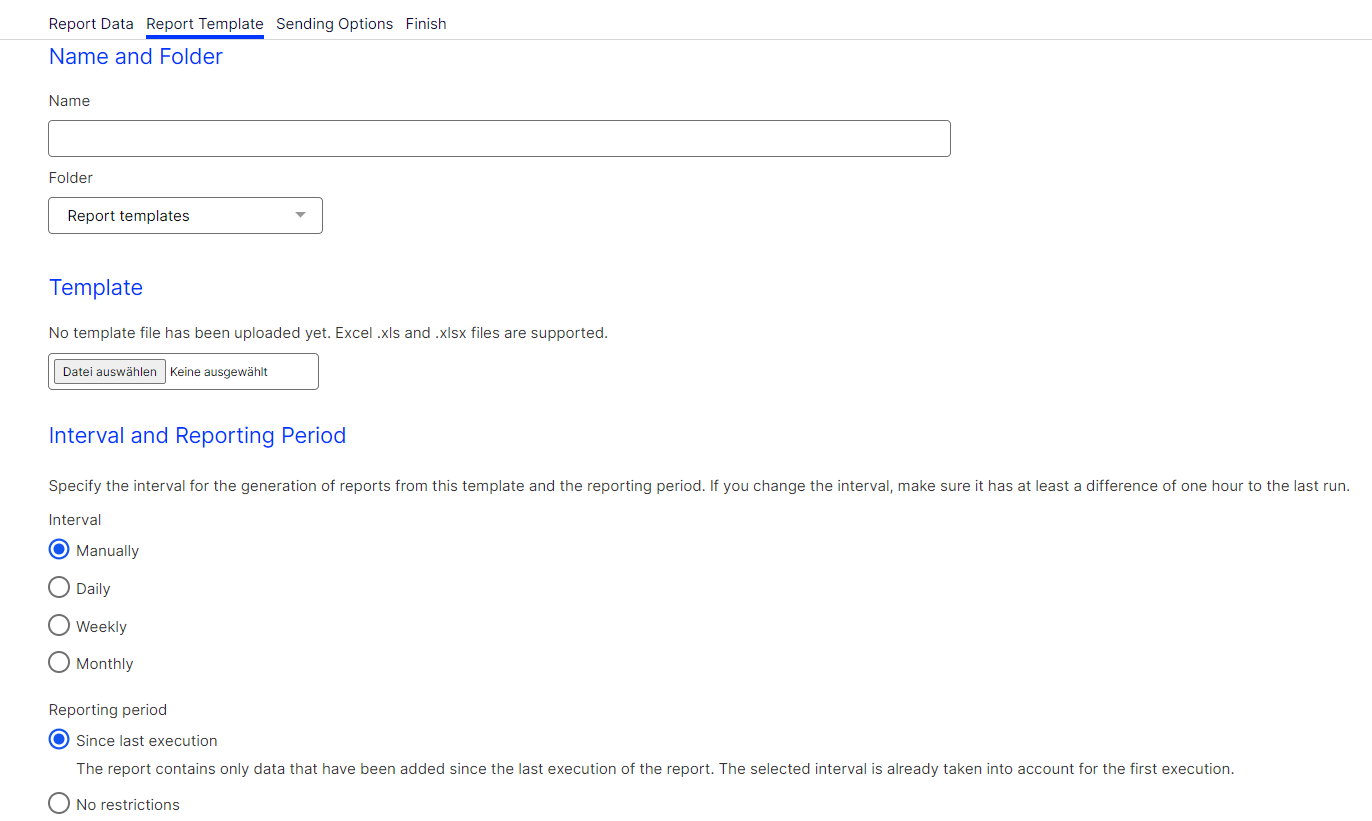
To configure the automatic execution and sending of your template, perform the following steps after adding measures and groupings:
- In the Create Report window, in the Report Data tab, click Save as Report Template.
- In the Name box, enter the name of the report template.
- In the Folder list, select a folder to which you want to save the report template. To use an Excel template, click Browse… and select a template. If no template is uploaded, the Optimizely default template is used.
- In the Interval area, click the interval for the generation of reports from this template. If you change the interval, make sure that the last execution has run at least one hour ago.
- Manually. Reports can only be executed manually.
- Weekly. Select the day of the week and the time of day when the report should be executed.
- Monthly. Select the day of the month and the time of day when the report should be executed.
- In the Reporting Period area, select one of the following options.
- Since last execution to define that the report contains only data added since the last execution of the report. The selected interval is already taken into account for the first execution. If you select the Weekly interval, a reporting period of one week is used for the first execution. If you change the weekly execution interval, such as from Monday to Wednesday, the next execution uses the reporting period beginning Wednesday of the previous week.
- No restrictions to define that available data is evaluated each time the report is being executed. By using this option, the amount of data to be evaluated can be very large. The execution of such reports may take some time.
- Click Sending Options.
Reporting Period
Reporting period lets you specify the time frame from which data used in the analysis is derived. The No restrictions option relates only to the previously-defined global report parameters and measured data. If you evaluate openings in a report and define that only mailings started in 2018 should be considered, openings for mailings of the year 2018 are counted. The Incremental option evaluates data added since the last execution of the report.
Step 3. Sending the report
If you do not want to send the reports via email, leave these fields empty.
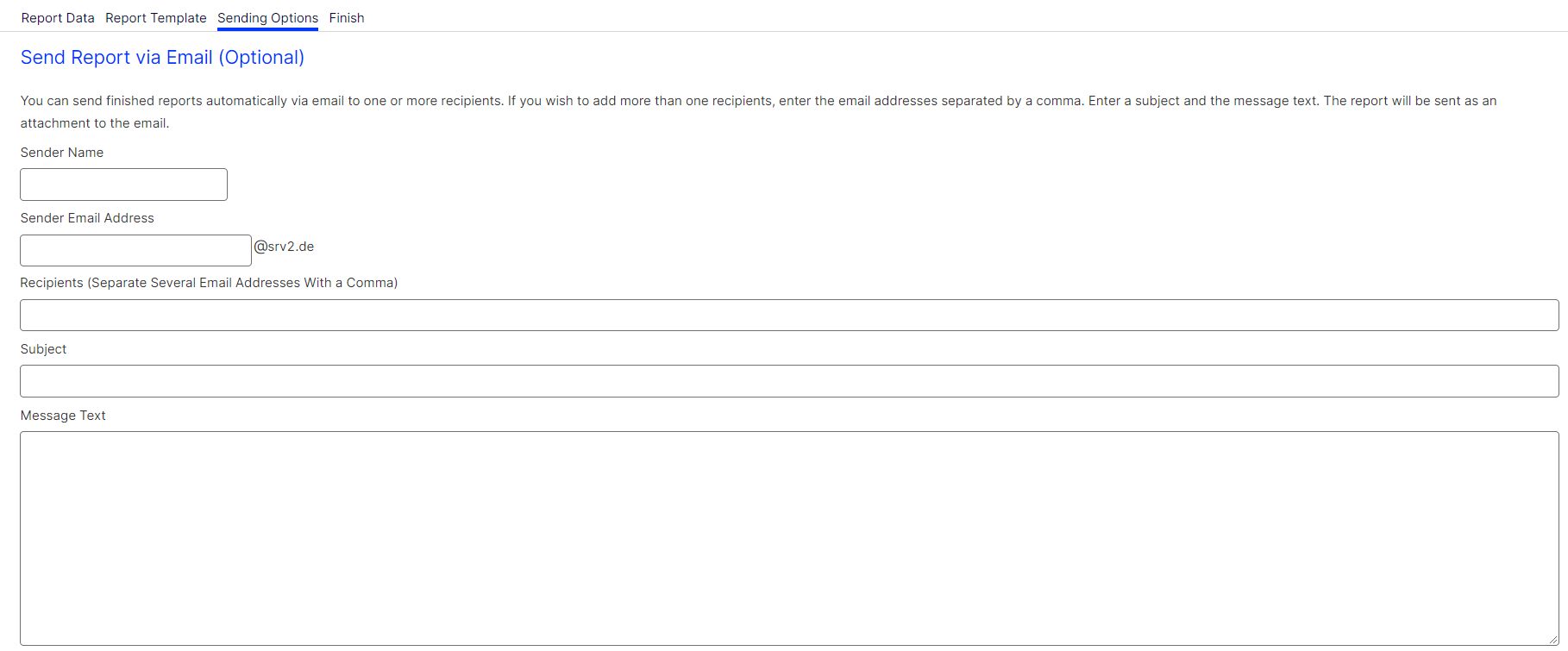
To send the report via email, perform the following steps:
- In the Recipients box, enter the email addresses of the recipients. Separate multiple email addresses with a comma.
- In the Subject box, enter the subject of the email.
- In the Message Text box, enter the message text of the email. Executed reports are attached as Excel files to the emails.
- Click Save.
- Close the window. The new report template appears in the upper section of the Deep Analytics window.
Executing ad hoc report
After performing the step 1 and step 2 to create a report template, you can execute the report without configuring or saving it as a template:
- In the Deep Analytics overview, click Execute Report Now….
- To use an Excel template, click Browse… and select a template. If you do not upload an Excel file, the default template is used.
- In the Reporting Period area, select one of the following options:
- Specify period. Specify the reporting period, a start date and an end date for the period you want to analyze.
- No restrictions. Define that all available data is analyzed at execution of the report. Note that by using this option the amount of data to be analyzed can be very large in the course of time. The execution of such reports may take some time.
- Click Sending Options and follow the steps under Sending options.
- Click Start Execution. After execution, the report is shown in the overview window and can also be downloaded as an Excel or CSV file.